A redirect in WordPress is like an address change. It helps your website guide users to a new location when the page they want to visit has been moved or replaced. Think of it as the way a post office forwards your mail when you change your address. There are different types of redirects, such as 301, 302, and 307. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll focus on 301 redirects since they indicate a permanent move to a new location. This guide to WordPress 301 Redirect provides comprehensive instructions on effectively implementing and managing 301 redirects in the WordPress platform.
What is a 301 Redirect and How Does it Work?
A 301 redirect informs web browsers and search engines that a web page has permanently moved to a new location. It ensures the traffic, ranking, and user experience of the old page are preserved by automatically directing visitors and search engine bots to the new page.
For instance, if you change a blog post URL from https://example.com/blog/seo-tips to https://example.com/blog/seo-best-practices, a 301 redirect ensures that visitors to the old URL are seamlessly redirected to the new one.
The 301 redirect works by informing the browser or search engine that the page is no longer available at the old URL and that they should go to the new URL to find it.
When to Use 301 Redirect?
Use a 301 redirect when your site or a page is relocated, or when you’re changing the permalink of a post or page. Failing to set up redirection can lead to a poor user experience, causing users to encounter a 404 error. This not only impacts user satisfaction but can also affect your WordPress SEO.
1) Moving Page Permanently to a New URL:
If you’ve changed a blog post URL, like from https://www.squarebeginners.com/remove-url-from-google-search/ to https://www.squarebeginners.com/remove-url-google/, use a 301 permanent redirect to ensure visitors are automatically directed to the new URL.
2)Deleting a Page on a Website:
When deleting a page, instead of showing a 404 error, use a 301 redirect to guide users to another relevant page, improving your site’s bounce rate.
3)Changing Your Website Structure:
For restructuring your website’s content, use a 301 redirect to seamlessly redirect traffic and ranking signals from the old URL to the new one.
4)Migrating Your Website to a New Domain:
During a website migration, a 301 redirect from the old domain to the new one preserves authority and facilitates a smooth rebranding.
5)Switching From HTTP to HTTPS Version:
To move from HTTP to HTTPS for security and Google recommendations, use a 301 redirect, e.g., redirecting http://www.mywebsite.com to https://www.mywebsite.com.
6)Switching from Non-WWW to WWW URLs (Fixing Duplication Issues) :
Use a 301 redirect to switch between www and non-www versions, avoiding duplicate content issues.
7)Combining Multiple Domains:
Merge multiple domains into one using a 301 redirect, but plan carefully to maintain SEO.
8)Solving ‘Trailing Slash’ Problems:
Address inconsistencies in handling trailing slashes with a 301 redirect for a more consistent user experience.
9)Fixing Upper-Case and Lower-Case Problems:
Ensure uniform case in URLs to avoid duplicate content issues with a 301 redirect.
How to Create 301 Redirects in WordPress?
Ensuring the correct implementation of a full site redirect in WordPress is crucial. To facilitate this process for beginners, we’ve outlined a step-by-step guide:
Creating 301 Redirects Using the Redirection Plugin
If you prefer a plugin-based approach to adding and managing redirects in WordPress, the Redirection plugin is a viable option.
-
- Begin by installing and activating the Redirection plugin. Detailed instructions on installing WordPress plugins can be found in our comprehensive guide.
- Begin by installing and activating the Redirection plugin. Detailed instructions on installing WordPress plugins can be found in our comprehensive guide.
Note: While setting up 301 redirects with a WordPress plugin is straightforward, it may introduce minor performance implications. Depending on your WordPress hosting provider, this method might result in redirects that are marginally slower than alternative methods.
-
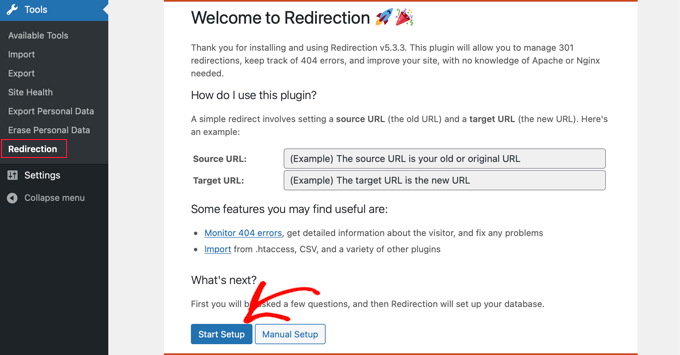
- Once activated, navigate to Tools » Redirection and click the ‘Start Setup’ button.
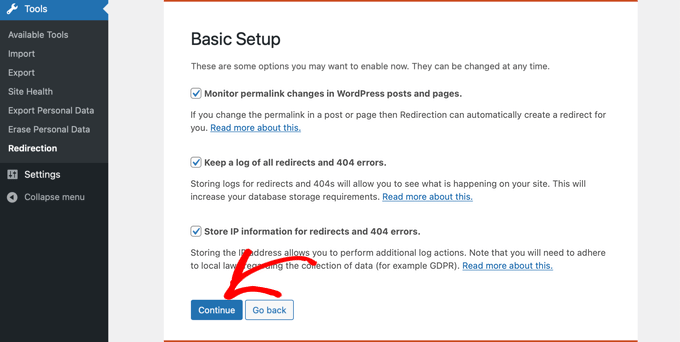
- Proceed through the setup by selecting options to monitor permalink changes and log all redirects and 404 errors. Enable these options and click ‘Continue Setup.’
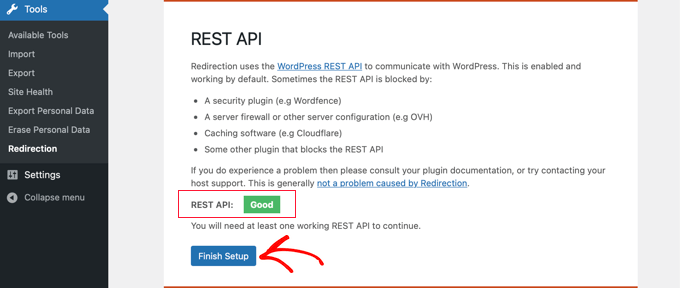
- The plugin will automatically test the Rest API. Once the status is confirmed as “Good,” click ‘Finish Setup.’
- The Redirection plugin will conduct additional tasks to complete its setup. Once the progress bar reaches 100%, click ‘Continue‘ and then ‘Ready to Begin.’
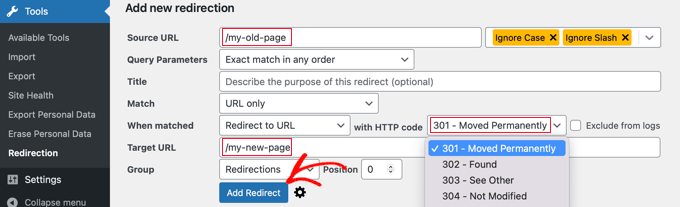
- With the setup complete, you can now create your 301 redirects. Go to Tools » Redirection in your WordPress panel and locate the ‘Add new redirection‘ section at the bottom of the screen.
Enter the Source URL of your old page, add the ‘Target URL‘ for redirection, and ensure the HTTP code option is set to ‘301 – Moved Permanently.’
- After entering the details, click ‘Add Redirect‘ to implement the redirection.
- Once activated, navigate to Tools » Redirection and click the ‘Start Setup’ button.
Creating 301 Redirects Using the Simple 301 Redirects Plugin
If simplicity is your priority in setting up 301 redirects, the Simple 301 Redirects plugin offers an uncomplicated solution.
- Install and activate the Simple 301 Redirects plugin on your WordPress website.
- Navigate to Settings » 301 Redirects.
- In the ‘Request‘ field, enter the old URL, and in the ‘Destination‘ field, provide the target URL.
- Click ‘Add New‘ to create the 301 redirect. Simple 301 Redirects will promptly initiate the redirection process
Best Practices and Common Mistakes
Below is a table outlining best practices and common mistakes related to 301 redirects:
| Aspect | Best Practices | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | – Create a comprehensive redirect plan before implementation. | – Neglecting to plan and map out all necessary redirects. |
| Accuracy | – Ensure accurate mapping from old URLs to new ones. | – Redirecting to irrelevant or incorrect destination URLs. |
| HTTP Status Code | – Use a 301 (Moved Permanently) status code for redirects. | – Using other status codes like 302 or 307 incorrectly. |
| Redirect Chains | – Avoid creating redirect chains; use direct mappings. | – Creating multiple sequential redirects for one URL. |
| Page Load Speed | – Minimize redirect chains to improve page load times. | – Using too many redirects, causing slower page loads. |
| Wildcards | – Use wildcards cautiously, and only when necessary. | – Overusing wildcards, leading to unintended redirections. |
| Relative vs Absolute URLs | – Use absolute URLs in the destination of the redirect. | – Using relative URLs, causing confusion or broken links. |
| Testing | – Test redirects thoroughly before implementing. | – Neglecting to test, leading to broken links and errors. |
| Monitoring | – Regularly monitor website analytics for any issues. | – Ignoring the need for ongoing monitoring and updates. |
| Communication | – Communicate changes to relevant stakeholders. | – Failing to inform marketing or other teams about redirects. |
| Update Sitemaps | – Update XML sitemaps to reflect the new URL structure. | – Forgetting to update sitemaps, causing indexing issues. |
| Server Configuration | – Configure server settings to handle redirects efficiently. | – Incorrect server configurations leading to errors. |
| Error Handling | – Implement custom error pages for improved user experience. | – Allowing default server error pages to be displayed. |
Remember that the effectiveness of 301 redirects relies on careful planning, accurate implementation, and ongoing monitoring to ensure a smooth transition for users and search engines.
Does 301 Redirect hurt SEO?
In general, implementing 301 redirects does not inherently hurt SEO (Search Engine Optimization). When used correctly, 301 redirects are a standard and recommended practice for handling URL changes, site migrations, or content restructuring. They indicate that a page has permanently moved to a new location, and search engines typically transfer the SEO value (link equity) from the old URL to the new one.
If 301 redirects are used correctly and thoughtfully, they should not hurt SEO. They are a valuable tool for managing site changes while preserving SEO value. It’s crucial to plan redirects carefully, test them thoroughly, and monitor their impact on search rankings and user experience.

![10 Best Redirect Plugins For WordPress [FREE] The Ultimate Guide to WordPress 301 Redirect](https://ehsandanish.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Redirection.png)
 Enter the Source URL of your old page, add the ‘Target URL‘ for redirection, and ensure the HTTP code option is set to ‘301 – Moved Permanently.’
Enter the Source URL of your old page, add the ‘Target URL‘ for redirection, and ensure the HTTP code option is set to ‘301 – Moved Permanently.’